Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2006;116(7):1776-1783. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI29044.
Abstract
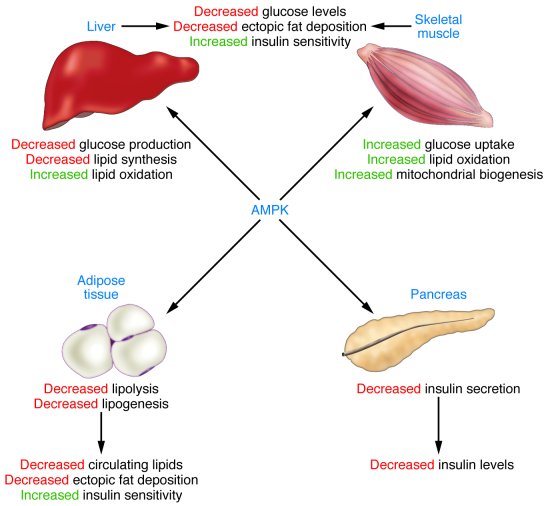
AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is an energy sensor that regulates cellular metabolism. When activated by a deficit in nutrient status, AMPK stimulates glucose uptake and lipid oxidation to produce energy, while turning off energy-consuming processes including glucose and lipid production to restore energy balance. AMPK controls whole-body glucose homeostasis by regulating metabolism in multiple peripheral tissues, such as skeletal muscle, liver, adipose tissues, and pancreatic β cells — key tissues in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. By responding to diverse hormonal signals including leptin and adiponectin, AMPK serves as an intertissue signal integrator among peripheral tissues, as well as the hypothalamus, in the control of whole-body energy balance.
Authors
Yun Chau Long, Juleen R. Zierath
Figure 2
Role of AMPK in the regulation of whole-body glucose homeostasis.



Copyright © 2025 American Society for Clinical Investigation
ISSN: 0021-9738 (print), 1558-8238 (online)