Anne Beigneux, … , Alan F. Hofmann, Stephen G. Young
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2002;110(1):29-31. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI16076.
Anne Beigneux, … , Alan F. Hofmann, Stephen G. Young
Published July 1, 2002
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2002;110(1):29-31. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI16076.
Abstract
Commentary
Authors
Anne Beigneux, Alan F. Hofmann, Stephen G. Young
Figure 1
Options:
View larger image
(or click on image)
Download as PowerPoint
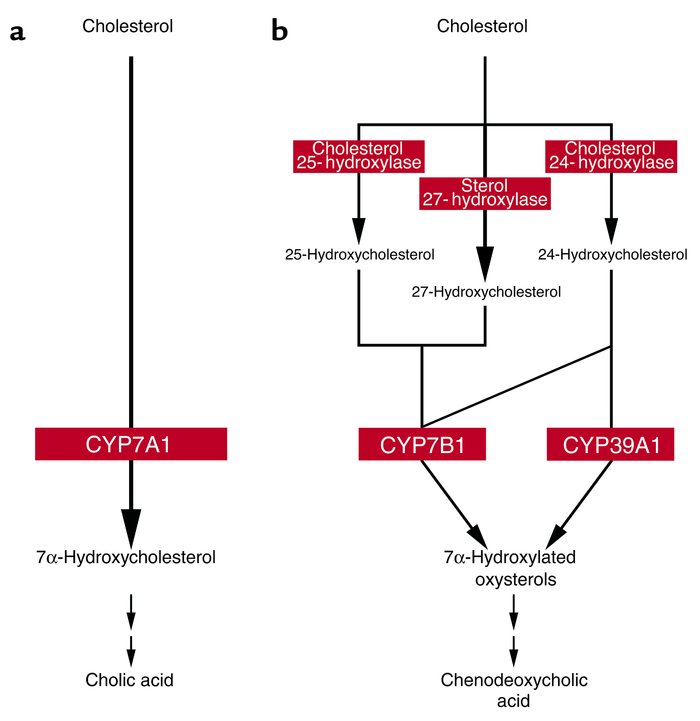
(a ) The classical pathway for bile acid synthesis begins with CYP7A1, which converts cholesterol into 7α-hydroxycholesterol. This pathway mainly produces cholic acid in humans. (b ) Alternate pathways for bile acid synthesis. Cholesterol is first converted into oxysterols by one of three different enzymes: sterol 27-hydroxylase (CYP27), expressed in multiple tissues including liver; cholesterol 25-hydroxylase, present at low levels in multiple tissues including heart, lung, and kidney; and cholesterol 24-hydroxylase (CYP46), expressed predominantly in the brain. Oxysterols are transported through the bloodstream to the liver, where they are 7α-hydroxylated by oxysterol 7α-hydroxylase (CYP7B1) in the case of 25- and 27-hydroxycholesterol and by CYP39A1 in the case of 24-hydroxycholesterol. Alternate pathways preferentially produce chenodeoxycholic acid in humans.



Copyright © 2025 American Society for Clinical Investigation
ISSN: 0021-9738 (print), 1558-8238 (online)